📖 INDEX
- Introduction to JavaScript
- What is JavaScript?
- History and Evolution of JavaScript
- Features of JavaScript
- Types of JavaScript Data (Primitive & Reference)
- Primitive Types
- Non-Primitive (Reference) Types
- Advantages of JavaScript
- Disadvantages of JavaScript
- JavaScript in Frontend Development
- Use Cases
- Examples
- JavaScript in Backend Development
- Use Cases
- Examples
- Frontend vs Backend JavaScript
- Asynchronous JavaScript: Callbacks, Promises & Async/Await
- Callbacks
- Promises
- Async and Await
- Real-World Applications of JavaScript
- Conclusion
1️⃣ Introduction to JavaScript
JavaScript is one of the most important and widely used programming languages in the world today. It plays a central role in building modern web applications and websites. Every time you interact with a webpage — clicking a button, submitting a form, watching a video, or scrolling content — JavaScript is often working behind the scenes.
Originally designed to make web pages more interactive, JavaScript has grown far beyond that. Today, it is used not only on the frontend (browser side) but also on the backend (server side), in mobile apps, desktop apps, games, APIs, cloud services, and even machine learning.
JavaScript is considered a core web technology, along with HTML and CSS:
- HTML → Structure of the webpage
- CSS → Style and layout
- JavaScript → Behavior and interactivity
Because of its versatility and massive ecosystem, JavaScript is often the first language beginners learn and one of the most valuable skills for professional developers.
2️⃣ What is JavaScript?
🔹 Definition
JavaScript is a high-level, interpreted, object-oriented, and event-driven programming language primarily used to create dynamic and interactive web applications.
🔹 Key Characteristics
- Runs in the browser and on servers (via Node.js)
- Supports object-oriented programming (OOP)
- Handles asynchronous operations efficiently
- Can manipulate HTML and CSS dynamically
- Works across all modern browsers
- Single-threaded but non-blocking
🔹 Simple Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="title">Hello</h1>
<button onclick="changeText()">Click Me</button>
<script>
function changeText() {
document.getElementById("title").innerText = "Welcome to JavaScript!";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
This small script changes the text on the webpage when the user clicks a button.
3️⃣ History and Evolution of JavaScript
🕰️ Timeline
- 1995 – Created by Brendan Eich at Netscape in just 10 days.
- Initially named Mocha, then LiveScript, finally JavaScript.
- Despite its name, JavaScript is not directly related to Java.
📜 ECMAScript Standard
JavaScript is standardized by ECMA International under the name ECMAScript (ES).
Key versions:
- ES5 (2009) – Strict mode, JSON support.
- ES6 / ES2015 – Major upgrade:
letandconst- Arrow functions
- Classes
- Modules
- Promises
- ES7+ – Async/await, optional chaining (
?.), nullish coalescing (??), and more.
Today, JavaScript continues to evolve every year with new features.
4️⃣ Features of JavaScript
✅ 1. Lightweight and Fast
JavaScript is lightweight and executes quickly in browsers and servers.
✅ 2. Interpreted Language
JavaScript does not require compilation. It runs line by line.
✅ 3. Object-Oriented
Supports:
- Classes
- Objects
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
✅ 4. Event-Driven
Responds to user actions like:
- Clicks
- Keystrokes
- Mouse movement
- Form submission
✅ 5. Asynchronous Programming
Supports:
- Callbacks
- Promises
- Async/await
This allows JavaScript to handle tasks like API calls without blocking the main thread.
✅ 6. Cross-Platform
Works on:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
- Mobile devices
- All modern browsers
✅ 7. Client-Side and Server-Side
Used in:
- Browsers (frontend)
- Servers (Node.js backend)
✅ 8. Dynamic Typing
No need to declare variable types.
let x = 10; // Number
x = "Hello"; // String
x = true; // Boolean
✅ 9. Rich Ecosystem
Huge libraries and frameworks:
- Frontend: React, Angular, Vue
- Backend: Express, NestJS
- Mobile: React Native, Ionic
- Desktop: Electron
✅ 10. DOM Manipulation
JavaScript can:
- Change text
- Add/remove elements
- Modify styles
- Animate elements
5️⃣ Types in JavaScript
JavaScript has two main categories of data types:
- Primitive (Value Types)
- Non-Primitive (Reference Types)
🔹 A. Primitive Data Types
Primitive types store simple values and are immutable.
1. Number
Represents integers and floating-point numbers.
let age = 25;
let price = 99.99;
2. String
Represents text.
let name = "John";
let greeting = 'Hello World';
3. Boolean
Represents true or false.
let isLoggedIn = true;
let isAdmin = false;
4. Undefined
A variable declared but not assigned.
let x;
console.log(x); // undefined
5. Null
Represents intentional absence of value.
let data = null;
6. BigInt
Represents very large integers beyond the Number limit.
let bigNumber = 123456789012345678901234567890n;
7. Symbol
Creates unique identifiers.
let id = Symbol("id");
🔹 B. Non-Primitive (Reference) Data Types
These store complex data and are mutable.
1. Object
let person = {
name: "Alice",
age: 30,
city: "London"
};
2. Array
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"];
3. Function
function greet() {
console.log("Hello!");
}
4. Date
let today = new Date();
5. RegExp (Regular Expression)
let pattern = /hello/i;
6️⃣ Advantages of JavaScript
✅ 1. Runs in Browser (No Installation)
Users don’t need to install anything — JavaScript runs directly in browsers.
✅ 2. Faster Execution
Runs on the client-side, reducing server load and improving performance.
✅ 3. Highly Versatile
JavaScript can be used for:
- Websites
- Web apps
- Mobile apps
- Desktop apps
- APIs
- Games
- IoT
✅ 4. Large Community and Ecosystem
Millions of developers, thousands of libraries, frameworks, and tools.
✅ 5. Easy to Learn
Simple syntax, beginner-friendly, and lots of learning resources.
✅ 6. Cross-Browser Compatibility
Works on all major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge.
✅ 7. Full-Stack Capability
Same language for frontend and backend.
✅ 8. Asynchronous and Non-Blocking
Handles multiple tasks efficiently without freezing the application.
7️⃣ Disadvantages of JavaScript
❌ 1. Browser Dependency
Different browsers may behave differently.
❌ 2. Security Risks
Client-side code is visible and can be exploited (XSS, CSRF).
❌ 3. Single-Threaded
Heavy computations can block execution (though Web Workers help).
❌ 4. Loose Typing
Dynamic typing may cause runtime errors.
let x = 5;
x = "five"; // No error, but can cause bugs later
❌ 5. Debugging Can Be Difficult
Asynchronous bugs and browser inconsistencies can be challenging.
❌ 6. SEO Issues (Without Server-Side Rendering)
JavaScript-heavy pages may not be indexed properly unless SSR is used.
8️⃣ JavaScript in Frontend Development
Frontend refers to everything users see and interact with in a browser.
🔹 Frontend Responsibilities
- UI interaction
- Form validation
- Animations
- DOM manipulation
- Fetching data from servers
- Single Page Applications (SPAs)
🧩 Frontend Use Cases with Examples
✅ 1. Form Validation
<form onsubmit="return validateForm()">
<input type="text" id="username" placeholder="Enter name">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<script>
function validateForm() {
let name = document.getElementById("username").value;
if (name === "") {
alert("Name is required!");
return false;
}
return true;
}
</script>
✅ 2. DOM Manipulation
<p id="demo">Hello</p>
<button onclick="changeText()">Click Me</button>
<script>
function changeText() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerText = "Welcome to JavaScript!";
}
</script>
✅ 3. Event Handling
<button id="btn">Click</button>
<script>
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click", function() {
alert("Button clicked!");
});
</script>
✅ 4. Fetching API Data (AJAX)
fetch("https://api.example.com/users")
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
✅ 5. Animations
<div id="box" style="width:100px;height:100px;background:red;"></div>
<script>
let box = document.getElementById("box");
box.style.transition = "1s";
box.style.transform = "translateX(200px)";
</script>
✅ 6. Single Page Applications (SPA)
Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue allow building SPAs.
Example (React-style logic):
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button>
9️⃣ JavaScript in Backend Development
With Node.js, JavaScript can run on servers.
🔹 Backend Responsibilities
- Handling HTTP requests
- Managing databases
- Authentication and authorization
- Business logic
- APIs and microservices
- File handling
🧩 Backend Use Cases with Examples
✅ 1. Creating a Server (Node.js)
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.write("Hello from server!");
res.end();
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server running on port 3000");
});
✅ 2. REST API with Express
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.get("/users", (req, res) => {
res.json([{ id: 1, name: "John" }]);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server started");
});
✅ 3. Handling POST Requests
app.use(express.json());
app.post("/login", (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
res.send("Login successful");
});
✅ 4. Database Operations (MongoDB Example)
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/mydb");
const UserSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
email: String
});
const User = mongoose.model("User", UserSchema);
const user = new User({ name: "Alice", email: "alice@example.com" });
user.save();
✅ 5. Authentication (JWT)
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: 123 }, "secretKey", { expiresIn: "1h" });
✅ 6. Middleware Example
function logger(req, res, next) {
console.log(req.method, req.url);
next();
}
app.use(logger);
✅ 7. File Upload
const multer = require("multer");
const upload = multer({ dest: "uploads/" });
app.post("/upload", upload.single("file"), (req, res) => {
res.send("File uploaded");
});
🔟 Frontend vs Backend JavaScript
| Feature | Frontend JavaScript | Backend JavaScript |
|---|---|---|
| Runs On | Browser | Server (Node.js) |
| Used For | UI, DOM, animations | APIs, databases |
| Frameworks | React, Vue, Angular | Express, NestJS |
| Database Access | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| File System Access | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Security Role | Client-side logic | Server-side logic |
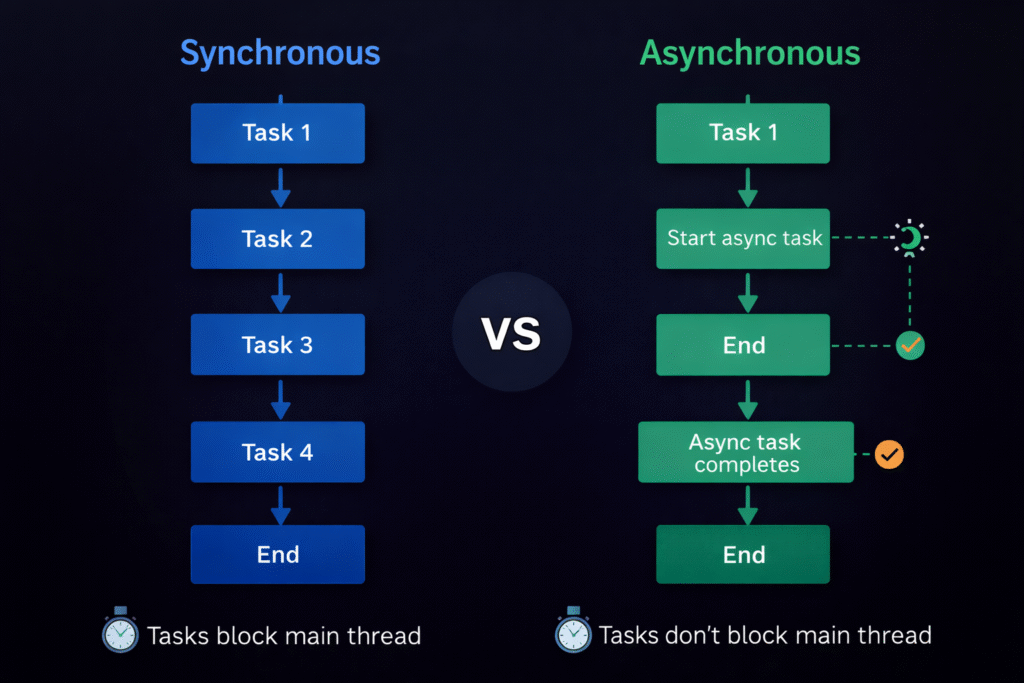
1️⃣1️⃣ Asynchronous JavaScript
JavaScript is single-threaded, meaning it executes one task at a time. However, it can handle long-running tasks (like API calls) without blocking the main thread using asynchronous programming.
There are three main ways to handle async operations:
- Callbacks
- Promises
- Async/Await
🔹 A. Callbacks
A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function and executed later.
function fetchData(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
callback("Data received");
}, 2000);
}
fetchData(function(result) {
console.log(result);
});
❌ Problem: Callback Hell (nested callbacks) makes code hard to read.
🔹 B. Promises
A Promise represents a value that may be available now, later, or never.
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let success = true;
if (success) {
resolve("Operation successful");
} else {
reject("Operation failed");
}
});
promise
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
🔹 C. Async and Await
async/await is built on top of promises and makes asynchronous code look synchronous.
✅ Basic Example
async function fetchData() {
return "Hello World";
}
fetchData().then(result => console.log(result));
✅ Using Await
function getData() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("Data received");
}, 2000);
});
}
async function displayData() {
let result = await getData();
console.log(result);
}
displayData();
✅ Real Example: Fetch API with Async/Await
async function fetchUsers() {
try {
let response = await fetch("https://api.example.com/users");
let data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
}
}
fetchUsers();
✅ Example in Backend (Node.js)
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.get("/users", async (req, res) => {
try {
const users = await getUsersFromDatabase();
res.json(users);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).send("Server error");
}
});
async function getUsersFromDatabase() {
return [{ id: 1, name: "John" }];
}
app.listen(3000);
🧠 Why Use Async/Await?
- Makes code easier to read
- Avoids
.then()chaining - Handles errors using
try/catch - Looks like synchronous code
1️⃣2️⃣ Real-World Applications of JavaScript
🌐 Websites
- YouTube
- Amazon
📱 Mobile Applications
- React Native
- Ionic
- NativeScript
🖥️ Desktop Applications
- Electron (VS Code, Slack, Discord)
🎮 Games
- Browser games
- Phaser.js
- Three.js (3D graphics)
🔌 APIs and Microservices
- REST APIs
- GraphQL
- Real-time services
🤖 AI and Machine Learning
- TensorFlow.js
- Brain.js
🛒 E-Commerce
- Payment gateways
- Shopping carts
- Inventory management
- Real-time notifications
📊 Data Visualization
- D3.js
- Chart.js
🌍 Internet of Things (IoT)
- Smart devices
- Home automation
- Sensors
1️⃣3️⃣ Conclusion
JavaScript is the backbone of modern web development. It enables developers to build dynamic, interactive, scalable, and high-performance applications across platforms using a single language.
From simple scripts to enterprise-level applications, JavaScript plays a crucial role in shaping the digital world. Its ability to work on both frontend and backend, along with its massive ecosystem, makes it one of the most valuable and in-demand skills today.
🔑 Key Takeaways
✔ JavaScript is versatile and powerful
✔ Works on both frontend and backend
✔ Supports asynchronous programming
✔ Has a huge ecosystem and community
✔ Essential skill for modern developers
✔ Continues to evolve with new standards
What are the main features of JavaScript?
JavaScript features include dynamic typing, async/await, closures, first-class functions, DOM manipulation, and modular code.
Why is JavaScript important for web development?
JavaScript enables interactive, dynamic, and real-time web applications across browsers, servers, mobile, and desktop platforms.
Does structured data improve SEO rankings?
Structured data helps search engines understand content and can improve click-through rates, but it does not directly increase rankings.
Should beginners learn these features?
Yes, learning these features early helps beginners write better code and prepare for real-world development.
