Introduction: The Web’s Ever-Evolving Landscape
In the fast-paced world of web development, staying ahead of the curve is not just an advantage – it’s a necessity. New technologies emerge, frameworks evolve, and the demands of users grow more sophisticated by the day. Amidst this constant flux, one particular combination of technologies has risen to prominence, empowering developers to build dynamic, high-performance, and scalable web applications with unprecedented efficiency: the MERN Stack.
If you’re a budding developer, a seasoned professional looking to upskill, or even just a curious individual wondering what powers many of your favorite websites, then you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will take you on an in-depth journey through the MERN Stack, demystifying its components, exploring its benefits, and equipping you with the knowledge to understand why it’s become a powerhouse in modern web development. Get ready to unlock the secrets of MERN Stack and discover how you can leverage its potential to create the next viral web application!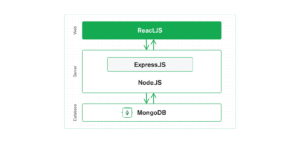
What Exactly Is the MERN Stack? A Deconstruction
The term “MERN” is an acronym, each letter representing a core technology that works in harmony to form a full-stack development environment. Let’s break down each component:
- M is for MongoDB: A NoSQL Database
- E is for Express.js: A Web Application Framework for Node.js
- R is for React.js: A JavaScript Library for Building User Interfaces
- N is for Node.js: A JavaScript Runtime Environment
Think of the MERN stack as a highly efficient assembly line for building web applications. Each component has a specialized role, yet they all speak the same language – JavaScript – making the development process incredibly streamlined.

Delving Deeper into Each MERN Stack Component
1. MongoDB: The Flexible Data Powerhouse
` What it is: MongoDB is a free and open-source NoSQL (Not Only SQL) database program. Unlike traditional relational databases (like MySQL or PostgreSQL) that store data in tables with predefined schemas, MongoDB is a document-oriented database. This means it stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents called BSON (Binary JSON), which can have varying structures.
Why it’s in MERN Stack:
- Flexibility and Scalability: The schema-less nature of MongoDB is a huge advantage for modern web applications where data structures can evolve rapidly. You don’t need to define a rigid schema upfront, allowing for faster iteration and development. It also scales horizontally with ease, making it ideal for applications with growing data demands.
- High Performance: MongoDB is designed for high performance, especially with large volumes of data and high traffic applications. Its ability to store related data together in a single document often reduces the need for costly joins, leading to faster data retrieval.
- JavaScript Native: Since MongoDB documents are JSON-like, they integrate seamlessly with JavaScript, the primary language of the MERN stack. This reduces the need for data translation layers and simplifies data manipulation.
- Cloud Compatibility: MongoDB Atlas, its fully managed cloud database service, makes it incredibly easy to deploy and scale your database in the cloud, further enhancing its appeal for modern web development.
Key Features of MongoDB:
- Document Model: Data stored in flexible JSON-like documents.
- Indexes: Supports various types of indexes to optimize query performance.
- Aggregation Framework: Powerful tools for data processing and analysis.
- Replication: Provides high availability and data redundancy.
- Sharding: Enables horizontal scaling across multiple servers.
2. Express.js: The Robust Backend Framework
` What it is: Express.js (often just called Express) is a minimalist and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. It’s the “E” in MERN and handles all the server-side logic, routing, and API endpoints for your application.
Why it’s in MERN Stack:
- Unopinionated and Flexible: Express gives developers a lot of freedom in how they structure their applications. It doesn’t enforce a strict set of rules, allowing for customization and integration with various tools and libraries.
- Fast Development: With its simple API and robust middleware support, Express significantly speeds up the development of server-side applications. It handles common tasks like routing, request parsing, and error handling with ease.
- Powerful Routing: Express provides a clear and intuitive way to define routes for different URLs, linking them to specific functions that handle requests and send responses. This is crucial for building well-structured APIs.
- Middleware Support: Middleware functions are functions that have access to the request object (
req), the response object (res), and the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. They can perform various tasks like logging, authentication, data validation, and more. This modular approach keeps your code clean and manageable. - JavaScript Everywhere: Being built on Node.js, Express allows developers to use JavaScript for both front-end and back-end development. This “full-stack JavaScript” approach simplifies context switching and allows for a more cohesive development team.
Key Features of Express.js:
- Routing: Defines how an application responds to a client request to a particular endpoint, which is a URI (or path) and a specific HTTP request method (GET, POST, etc.).
- Middleware: Functions that execute in the middle of the request-response cycle.
- Template Engines: Supports various template engines (like Pug, EJS, Handlebars) for generating dynamic HTML.
- Error Handling: Provides robust mechanisms for handling errors gracefully.
3. React.js: The Dynamic User Interface Builder
` What it is: React.js (often just React) is a declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Developed by Facebook (now Meta), it allows developers to create reusable UI components, making complex UIs easier to manage and develop. It’s the “R” in MERN Stack and is responsible for everything the user sees and interacts with in the browser.
Why it’s in MERN Stack:
- Component-Based Architecture: React’s core philosophy revolves around building UIs with independent, reusable components. This modularity makes development faster, easier to maintain, and promotes code reusability across different parts of an application.
- Declarative Views: React makes it painless to create interactive UIs. You simply describe what your UI should look like for a given state, and React efficiently updates and renders just the right components when your data changes.
- Virtual DOM: React uses a “Virtual DOM” (Document Object Model) to optimize rendering performance. Instead of directly manipulating the browser’s DOM (which can be slow), React first updates a lightweight representation of the DOM in memory. It then efficiently calculates the minimal changes needed and updates only those parts of the real DOM, leading to incredibly fast and smooth user experiences.
- Unidirectional Data Flow: React typically follows a unidirectional data flow (parent-to-child components), which makes data management predictable and debugging easier.
- Rich Ecosystem: React boasts a massive and vibrant community, offering a plethora of tools, libraries, and resources (like Redux for state management, React Router for navigation, Next.js for server-side rendering).
Key Features of React.js:
- JSX: A syntax extension for JavaScript that allows you to write HTML-like code directly within your JavaScript.
- Components: Reusable, self-contained building blocks for your UI.
- State and Props: Mechanisms for managing data within and between components.
- Lifecycle Methods/Hooks: Functions that allow you to tap into specific points in a component’s lifecycle (e.g., when it mounts, updates, or unmounts).
- Context API: A way to share values like user data or theme preferences between components without explicitly passing props through every level of the component tree.
4. Node.js: The JavaScript Runtime Environment
` What it is: Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment that executes JavaScript code outside of a web browser. While browsers typically run JavaScript on the client-side, Node.js allows JavaScript to be used for server-side programming, command-line tools, and more. It’s the “N” in MERN Stack and is the foundation upon which Express.js is built.
Why it’s in MERN Stack:
- Full-Stack JavaScript: This is perhaps the most significant advantage. With Node.js, you can use JavaScript for both your front-end (React) and back-end (Express). This eliminates the need for developers to context-switch between different languages, simplifying development, reducing cognitive load, and enabling better collaboration within a team.
- Asynchronous and Event-Driven: Node.js operates on an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. This makes it incredibly efficient for handling many concurrent connections, making it ideal for real-time applications, APIs, and microservices.
- Fast Performance: Built on Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, Node.js compiles JavaScript code into machine code, resulting in very fast execution speeds.
- Rich Ecosystem (NPM): Node.js comes with npm (Node Package Manager), the largest ecosystem of open-source libraries in the world. This provides developers with a vast collection of pre-built modules and tools, significantly accelerating development.
- Scalability: Node.js is well-suited for building scalable network applications that can handle a large number of concurrent connections efficiently.
Key Features of Node.js:
- V8 Engine: Utilizes Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine for high-performance code execution.
- Non-Blocking I/O: Enables efficient handling of multiple operations without waiting for each to complete.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Based on an event loop that processes events and callbacks.
- NPM: The world’s largest package manager for JavaScript libraries and tools.
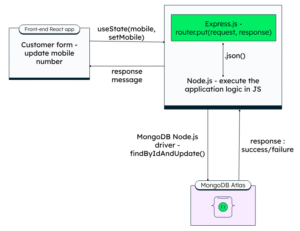
How the MERN Stack Works Together: The Data Flow
Imagine a user interacting with a MERN Stack application. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the data flow:
- Client-Side (React.js): The user interacts with the beautifully rendered UI built with React. When the user performs an action (e.g., clicks a button, submits a form), React captures this event.
- API Request: React then makes an HTTP request (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to the backend server. This request typically targets a specific API endpoint.
- Server-Side (Express.js on Node.js): The Node.js server, powered by Express.js, receives this request. Express’s routing mechanism directs the request to the appropriate handler function.
- Database Interaction (MongoDB): The handler function, often acting as a controller, then interacts with the MongoDB database. It might query for data, insert new data, update existing data, or delete data, depending on the request.
- Data Response: MongoDB returns the requested data (or a confirmation of the operation) to the Express.js server.
- API Response: Express.js processes this data and constructs an HTTP response, typically in JSON format.
- Client-Side Update (React.js): React receives the JSON response from the server. Based on this new data, React updates the relevant parts of the UI, re-rendering only the components that need to change. The user sees the immediate effect of their action.
This seamless communication, all within the JavaScript ecosystem, is what makes the MERN stack so powerful and efficient.
Why Choose the MERN Stack? The Undeniable Advantages
The popularity of the MERN stack isn’t just a trend; it’s a testament to its significant advantages in modern web development.
- Full-Stack JavaScript (The “One Language” Advantage): This is arguably the biggest selling point. Using JavaScript for the entire application stack (front-end, back-end, and even database interactions with MongoDB’s JSON-like documents) streamlines the development process.
- Reduced Context Switching: Developers don’t need to switch between different languages and syntaxes, leading to faster development and fewer errors.
- Easier Code Sharing: Components, utility functions, and even validation logic can sometimes be shared between the front-end and back-end.
- Simplified Team Collaboration: Teams can specialize in full-stack JavaScript rather than having separate front-end (e.g., Python/Ruby) and back-end (e.g., PHP) teams, leading to more cohesive development.
- Robust and Modern Technologies: Each component of the MERN stack is a leading technology in its respective domain, backed by strong communities and continuous development.
- MongoDB: Offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability for data storage.
- Express.js: Provides a fast, unopinionated, and feature-rich framework for building APIs.
- React.js: Delivers dynamic, high-performance user interfaces.
- Node.js: Ensures efficient, scalable server-side execution.
- Cost-Effective and Open Source: All technologies in the MERN stack are open-source and free to use, significantly reducing development costs. This makes it an attractive option for startups and budget-conscious projects.
- High Performance and Scalability:
- Node.js’s Non-Blocking I/O: Enables handling a large number of concurrent requests efficiently, making it suitable for real-time applications and high-traffic websites.
- MongoDB’s Horizontal Scaling: Allows databases to scale out easily by distributing data across multiple servers.
- React’s Virtual DOM: Optimizes UI rendering for a smooth user experience.
- Extensive Community Support and Ecosystem: Each technology in the MERN stack benefits from a massive and active community.
- Vast Libraries and Tools: npm (Node Package Manager) offers an incredibly rich ecosystem of open-source packages and tools for Node.js and React.
- Abundant Resources: Extensive documentation, tutorials, forums, and online communities make learning and troubleshooting much easier.
- Continuous Innovation: The active communities ensure that the technologies are constantly updated and improved.
- Rapid Development: The combination of powerful tools, a unified language, and extensive libraries allows developers to build and deploy applications much faster. This agility is crucial in today’s competitive market.
- Ideal for Single-Page Applications (SPAs): React.js is perfectly suited for building SPAs, where the entire application loads a single HTML page and dynamically updates content as the user interacts. MERN provides an excellent backend for feeding data to these SPAs.
Potential Downsides and Considerations
While the MERN stack offers numerous benefits, it’s also important to be aware of potential challenges:
- Learning Curve: For beginners, mastering all four technologies, especially React.js with its component-based architecture and state management, can have a steeper learning curve compared to simpler frameworks.
- NoSQL Challenges: While MongoDB’s flexibility is a strength, its schema-less nature can sometimes be a challenge for applications requiring strict data integrity and complex relational queries. Designing an efficient NoSQL schema requires a different mindset than traditional SQL databases.
- Performance for CPU-Bound Tasks: While Node.js excels at I/O-bound tasks, it’s not always the best choice for heavily CPU-bound operations due to its single-threaded event loop. For such tasks, other languages might offer better performance. However, solutions like worker threads can mitigate this to some extent.
- Tooling Overload: The vast ecosystem, while a benefit, can also be overwhelming. Choosing the right state management library, bundler, or testing framework can be a daunting task for new developers.
Use Cases: Where MERN Stack Shines Brightest
The MERN stack is incredibly versatile and well-suited for a wide range of web applications:
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs): Blogs, portfolios, dashboards, and interactive tools.
- E-commerce Platforms: Building dynamic product catalogs, shopping carts, and checkout processes.
- Social Media Applications: Handling user profiles, feeds, real-time updates, and messaging.
- Real-time Chat Applications: Leveraging Node.js’s event-driven architecture for instant messaging.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Creating robust and flexible platforms for managing content.
- Interactive Dashboards and Data Visualization: Building dynamic interfaces for displaying and analyzing data.
- RESTful APIs: Developing powerful backend APIs to serve data to various clients (web, mobile, IoT).
- Streaming Applications: Handling concurrent connections and data streams efficiently.
`
Getting Started with MERN Stack: Your First Steps
Ready to dive into MERN development? Here’s a roadmap to get you started:
- Master JavaScript Fundamentals: A strong grasp of modern JavaScript (ES6+ features) is paramount.
- Learn Node.js Basics: Understand how Node.js works, its module system, and the npm package manager.
- Explore Express.js: Learn how to set up an Express server, define routes, use middleware, and build RESTful APIs.
- Dive into MongoDB: Familiarize yourself with MongoDB’s document model, basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, and Mongoose (an ODM for Node.js and MongoDB).
- Conquer React.js: Understand components, JSX, state, props, lifecycle methods/hooks, and potentially a state management library like Redux or Context API.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The best way to learn is by building projects. Start with simple applications and gradually increase complexity.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced MERN Concepts
Once you’ve grasped the fundamentals, you can explore more advanced topics to enhance your MERN applications:
- State Management (Redux/Context API): For managing complex application states in React.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implementing secure user login and access control (e.g., JWT).
- Deployment: Learning how to deploy your MERN application to cloud platforms (AWS, Google Cloud, Heroku, Vercel).
- Testing: Writing unit, integration, and end-to-end tests for your MERN application.
- WebSockets (Socket.io): For building real-time, bidirectional communication features.
- Server-Side Rendering (Next.js/Gatsby): For improving SEO and initial load performance of React applications.
- Containerization (Docker): Packaging your application and its dependencies into isolated containers.
- Microservices Architecture: Breaking down a large application into smaller, independent services.
The Future of MERN Stack Development
The MERN stack continues to evolve at a rapid pace. With ongoing advancements in JavaScript, Node.js, React, and database technologies, its future looks incredibly bright. The trend towards full-stack JavaScript development is only strengthening, and MERN remains at the forefront of this movement.
The continuous innovation in tools and libraries within the JavaScript ecosystem, combined with the growing demand for dynamic and scalable web applications, ensures that MERN developers will remain highly sought after in the industry for years to come.
Conclusion: Your Gateway to Modern Web Development
The MERN stack is more than just a collection of technologies; it’s a philosophy of web development that prioritizes efficiency, scalability, and a unified language experience. By mastering MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js, you equip yourself with the tools to build virtually any modern web application, from intricate e-commerce platforms to real-time communication tools.
2 thoughts on “Ultimate Guide to MERN Stack Development-1”